Are you looking to improve your software development workflow? Git might be just the tool you need! As a version control system, Git helps developers track and manage changes to their codebase, collaborate more effectively with teammates, and ensure code quality and consistency.
By using Git, you can easily:
1 -Create and switch between branches to isolate changes and experiment with new features.
2 – Merge changes from multiple branches back into your main codebase.
3 – Roll back changes to specific versions of your code.
4 – Collaborate with other developers by sharing code and reviewing changes.
List of Git Commands:
Below is the list of some of the most used Git Commands along with a short description:
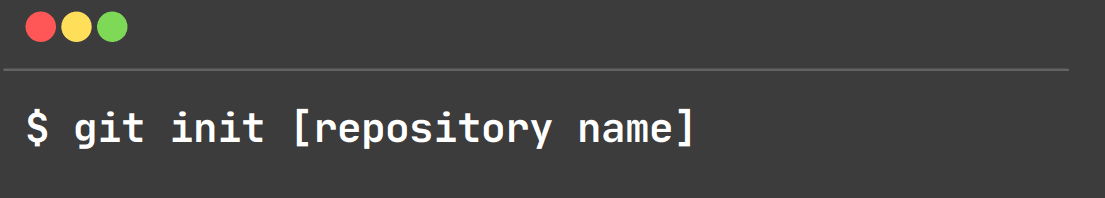
git Init:
This command is used to start a new repository. Git creates a .git directory.
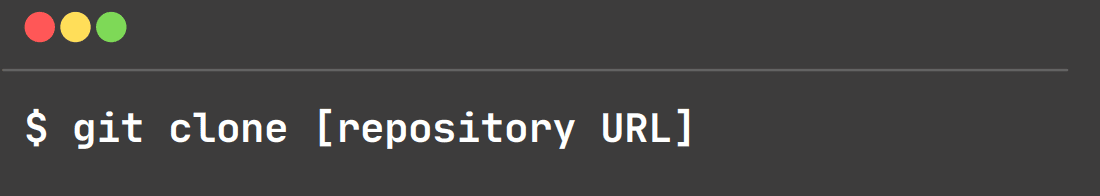
git clone:
This command is used to obtain a repository from an existing GitHub repo.
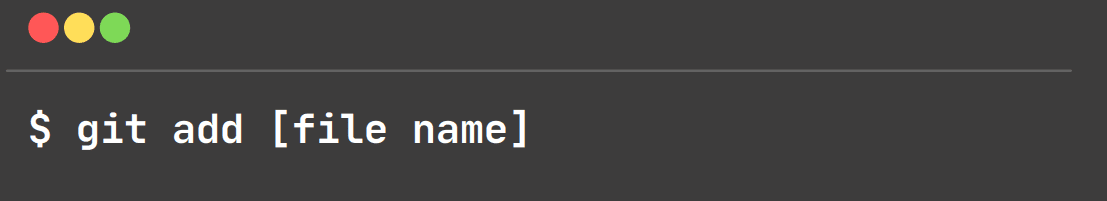
git add:
This command is used to add a file to the staging area.
git add. :
This command is used to add all the files to the staging area.

git commit:
This command takes a snapshot of the project’s currently stagged changes.

git diff:
This command shows the file difference which are not yet stagged.

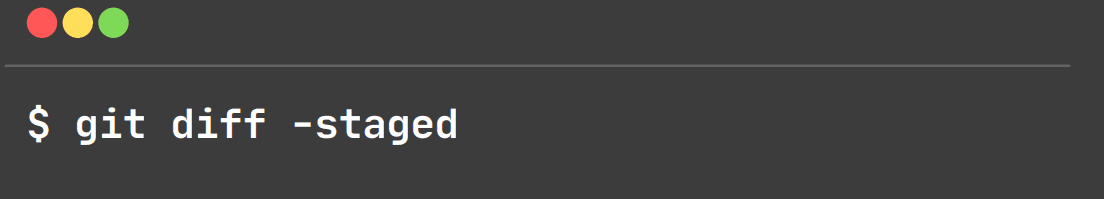
git diff-staged:
This command shows the differences between files in the staging area and the latest version present.
git status:
This command shows all the modified files which are not committed.

git log:
This command shows the list of version history.

git branch:
This command shows all the branches of the repository.

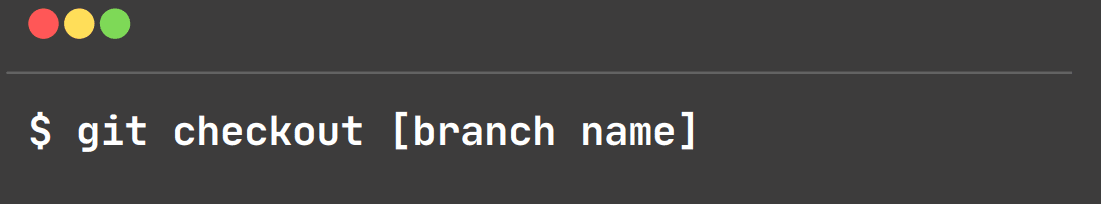
git checkout:
This command is used to switch between branches.
git checkout -b:
To create a new branch and switch to that.

git push:
This command sends all the committed changes to your repository.

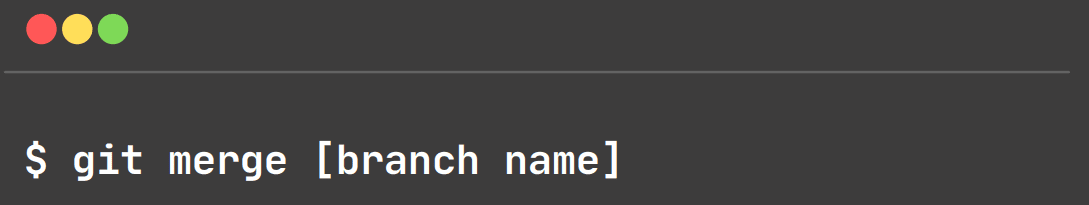
git merge:
This command shows all the branches of the repository.
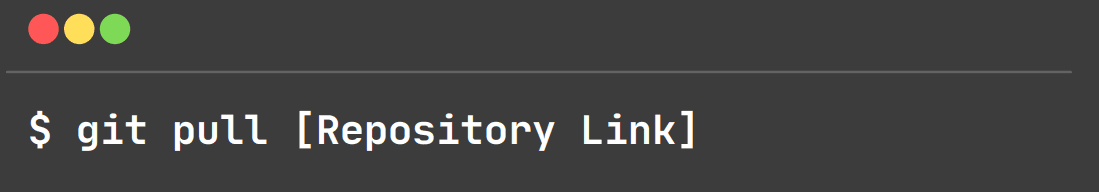
git pull:
This command fetch and merge changes.
git stash:
This command temporarily stores all the modified tracked files

I hope you guys find this tutorial helpful. If you do please share it with your friends and bookmark this site for more amazing tutorials. Thanks

